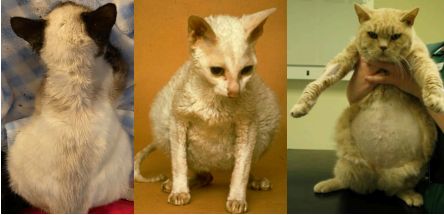
Wet FIP
The most common form of the disease is referred to as “wet FIP.” Wet FIP tends to be more acute in onset and is accompanied by: Cats with abdominal effusions usually manifest with abdominal swelling, while cats with thoracic (chest) effusions often manifest breathing problems (dyspnea). Many of these cats will be noticeably jaundiced due to high levels of bilirubin and/ or have strongly yellow-tinged serum and urine.
• Lethargy
• Sneezing, watery eyes, nasal discharge
• Loss of interest in food
• Not playing
• Not socializing
• Excessive sleeping
• Not jumping or climbing
• Weight loss
• Fever unresponsive to antibiotics
• Jaundice (yellowing in the eyes and skin caused by the destruction of red blood cells)
• Severe anemia (Hematocrit or Hct of 20% is concerning; Hct 15% or less is an EMERGENCY)
• Stunted growth